What is RHEL?
Red Hat Enterprise Linux, or RHEL, is a Linux distribution crafted by Red Hat specifically for the business world. It’s celebrated for its stability, security, and robust performance, making it a go-to platform for everything from simple web servers to complex, multi-tiered applications.

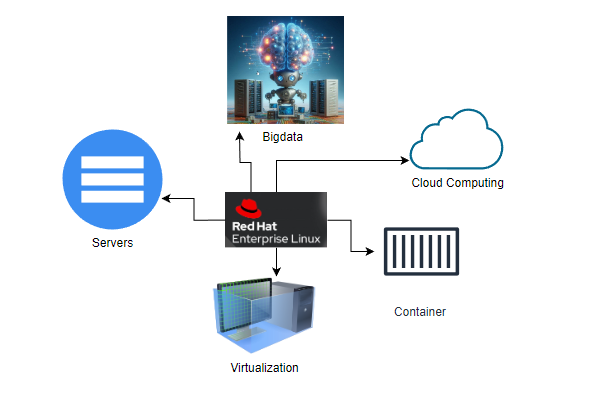
Various Uses of RHEL
- Servers: RHEL is a staple in server environments, excelling in web hosting, database management, and application servers.
- Cloud Computing: It’s a top choice for cloud setups, whether private, public, or hybrid.
- Virtualization: With strong support for virtualization technologies, RHEL is perfect for virtualized environments.
- Development: It offers a secure and stable platform for software development and testing.
- Big Data: RHEL’s scalability and performance make it ideal for big data applications.
- Containerization: Integrated support for Docker and Kubernetes makes RHEL a solid choice for containerized applications.
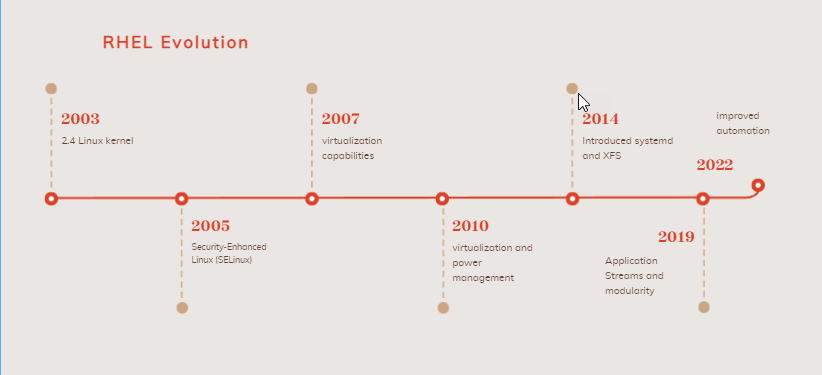
RHEL has evolved through several key versions:
- RHEL 3 (2003): Introduced with the 2.4 Linux kernel.
- RHEL 4 (2005): Based on the 2.6 Linux kernel, introducing Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux).
- RHEL 5 (2007): Added virtualization capabilities using Xen.
- RHEL 6 (2010): Enhanced with the 2.6.32 Linux kernel, improving virtualization and power management.
- RHEL 7 (2014): Introduced systemd and XFS as the default file system, based on the 3.10 Linux kernel.
- RHEL 8 (2019): Featured the 4.18 Linux kernel, bringing Application Streams and modularity.
- RHEL 9 (2022): Focused on enhanced security features and improved automation.
RHEL is one of the most popular enterprise Linux distributions because of:
- Enterprise Support: Red Hat offers comprehensive support and services.
- Security: Regular updates and patches ensure strong security.
- Stability: It’s incredibly stable, ideal for mission-critical applications.
- Certifications: RHEL is certified on a wide range of hardware and software platforms.
- Community: It boasts a strong community and ecosystem, including the Fedora Project, which serves as its upstream source.
Importance of Upgrading RHEL Versions
- Security: Newer versions come with enhanced security features and timely patches.
- Performance: Each release brings performance improvements.
- Compatibility: Staying current ensures compatibility with the latest applications and hardware.
- Features: Access to new capabilities that boost productivity and efficiency.
- Support: Red Hat offers support for a limited time on each version, so upgrading is essential for continued support.
If you have many applications running on RHEL, upgrading requires careful planning:
- Assessment: Evaluate your current environment and identify the applications running on RHEL.
- Compatibility Check: Ensure all applications and dependencies are compatible with the new RHEL version.
- Backup: Perform a full backup to prevent data loss.
- Testing: Set up a test environment to simulate the upgrade process and test applications.
- Plan the Upgrade: Develop a detailed upgrade plan, including timelines, resources, and rollback procedures.
- Staging: Perform the upgrade in a staging environment first to ensure a smooth transition.
- Incremental Upgrade: Upgrade systems incrementally to minimize risk.
- Monitoring: Keep a close eye on the system and applications post-upgrade.
- Documentation: Document the entire process, noting any issues and their resolutions.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) is a cornerstone of enterprise computing, offering unparalleled stability, security, and support for a vast range of applications. Whether you’re running web servers, deploying cloud solutions, or handling big data, RHEL ensures your business operates smoothly and efficiently.
As RHEL evolves, it brings new features, improved performance, and fortified security. Upgrading to the latest version isn’t just a technical necessity—it’s a strategic move to stay ahead in the fast-paced tech world. By carefully planning and executing your upgrade, especially in environments with many applications, you can minimize disruption and maximize benefits.